Satellite Imagery
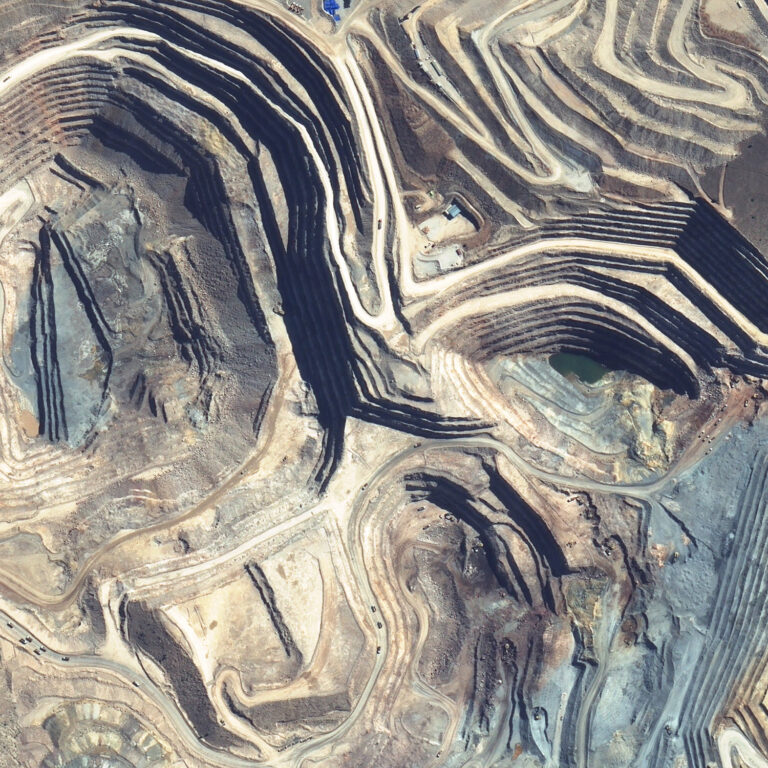
PhotoSat uses stereo satellite imagery from high-resolution optical satellites to produce elevation surveys of mine sites, infrastructure projects, inundation areas, and more. PhotoSat works with new or archive satellite imagery from many sources, including Maxar’s WorldView satellites and Airbus’ Pleiades and Neo satellites.